
Electrical installations must function smoothly and always be available. However, protection against electric shock is important. In the event of a fault, residual current devices (RCDs) provide effective protection against indirect and direct contact as well as fire protection by disconnection within a very short time.
Especially in the production process, unplanned disconnection of installation parts usually leads to production stoppage as well as equipment damage and jeopardise not only the process reliability but also the quality of the goods to be produced. The result is unforeseeable additional costs for companies.
Therefore, it is important not only to interrupt the power supply with suitable protective devices when residual currents are actually present, but also to detect emerging residual currents at an early stage. Because only those who keep a permanent eye on their electrical installation can react in time without the protective device disconnecting. For this purpose, a combination of residual current monitoring and residual current protective device is suitable, e.g. MRCDs (Modular Residual Current protective Devices) from Bender.
RCD (Residual Current Device) is the general term for all types of residual current protective devices. In addition to the well-known RCCBs and RCBOs, this product group also includes CBRs and the so-called MRCDs. All the devices mentioned above can detect a residual current and disconnect the monitored circuit in the event of a fault. A required disconnection according to DIN VDE 0100-410 takes place. These devices are prescribed or recommended in many areas (DIN VDE 0100-530).
The general difference between MRCD and RCM is that the Residual Current Monitor (RCM) is for monitoring purposes and the MRCD for protection purposes. Due to this, MRCDs are characterised by the fact that they trip a connected circuit breaker with isolating properties in a normatively specified, very short time in order to interrupt the power supply in time when a fault occurs. Accordingly, MRCDs are particularly reliable and especially fast in tripping compared to RCMs.
Taking into account the maximum switching time (DIN VDE 0100-410), the MRCD conforms to DIN EN 60947-2 Annex M as a protective device with which, among other things, the following protection goals can be fulfilled:
Similar to an RCM, an MRCD from Bender also continuously monitors the electrical installation and issues an alarm when a residual current occurs. However, unlike the RCM, the Bender MRCD switches a potential-free contact when the set response value is exceeded, which leads to a safe disconnection of the circuit breaker connected to the MRCD within the time required by the standard.
Continuous monitoring and prewarning bring further advantages to the operators of electrical installations in particular, such as:
In industrial applications, an MRCD solution can often be used. The prerequisite for this is that the MRCD is only accessible to instructed or electrically skilled persons (DIN VDE 0100-530). Therefore, according to DIN VDE 0100-530, it is clear: An MRCD solution must not be used for domestic installations.
The use of an MRCD is particularly advisable if the operating current can no longer be conducted via the terminals of an RCCB solution or if very high voltages and/or load currents may occur.
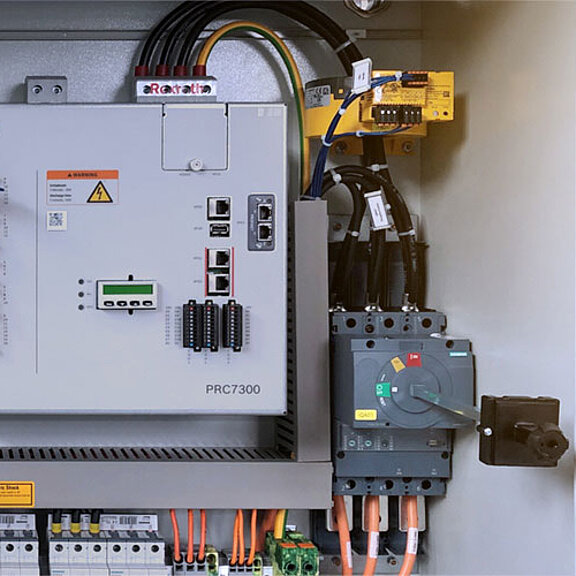
Bender is expanding its residual current portfolio with modular sensors and devices from the new SensorPRO series. One component of this modular series are AC/DC sensitive devices for use as modular residual current devices – type B MRCDs – in accordance with the currently valid version of the IEC 60947-2 Annex M standard. They can be used as additional protection (protection against indirect contact) in earthed systems (TN and TT systems) in which DC residual currents or AC residual currents can occur.

Beispiel für die Zusammenstellung eines MRCD-Moduls
In conjunction with a suitable disconnecting device for personal, fire or plant protection, they can be used in industrial environments and combine measuring current transformers and evaluation electronics so that an additional evaluator is no longer necessary.
The integrated relays can be used to control the disconnecting device and issue a prewarning. Furthermore, the Modbus interface offers the possibility of continuously monitoring the leakage and fault currents of the system in a higher-level monitoring system and, if necessary, analysing them.
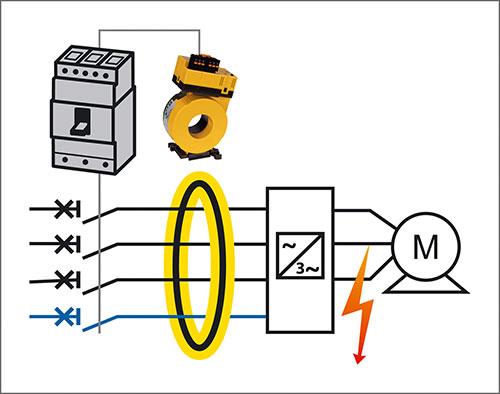
Applikationsbeispiel:
Allstromsensitives modulares Fehlerstromgerät (Typ B) MRCDB303 mit integriertem Messstromwandler kombiniert mit Leistungsschalter. Einstellbarer Ansprechbereich 30 mA ... 3 A; flexibel anpassbar auf anlagenbedingte Ableitströme.
Due to the optionally available, fully shielded transformer modules, the new MRCDs are optimally suited for special applications with high and rapidly changing inrush and pulse currents (e.g. various welding applications); false tripping in installations is therefore avoided. The frequency range of up to 100 kHz ensures that the requirements of the IEC 60364-4-42 standard and those of the VdS (VdS 2033) in the area of fire protection are fully met, so that the devices are also predestined for use in fire-hazardous operating sites, such as sawmills or other companies in the woodworking industry.
With the use of an MRCD type B from Bender, personal protection, fire protection and plant protection are possible without immediate disconnection and are no longer an issue.
Januar 2021
Marita Schwarz-Bierbach, MC-CCC
Bender GmbH & Co. KG, Grünberg
| Name | Category | Size | Language | Timestamp | D-/B-Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRCD | Flyer | 96.3 KB | EN | 2021/05/1818.05.2021 |
Products

AC/DC sensitive residual current monitoring modules for MRCD applications

Modular residual current device type B for additional protection (protection against indirect contact) in earthed systems (TN and TT systems)

AC/DC sensitive residual current monitoring modules for MRCD applications

Modular residual current device type B for additional protection (protection against indirect contact) in earthed systems (TN and TT systems)